本节提供解决配置缓存问题的通用指南,无论是你的构建逻辑还是 Gradle 插件中的问题。
使用配置报告
当 Gradle 在序列化执行任务所需的必要状态时遇到问题,它会生成一份 HTML 报告,详细说明检测到的问题。控制台输出中包含一个可点击的链接,指向此报告,允许你调查根本原因。
考虑以下包含两个问题的构建脚本:
tasks.register("someTask") {
val destination = System.getProperty("someDestination") (1)
inputs.dir("source")
outputs.dir(destination)
doLast {
project.copy { (2)
from("source")
into(destination)
}
}
}tasks.register('someTask') {
def destination = System.getProperty('someDestination') (1)
inputs.dir('source')
outputs.dir(destination)
doLast {
project.copy { (2)
from 'source'
into destination
}
}
}运行任务失败,输出如下:
❯ ./gradlew --configuration-cache someTask -DsomeDestination=dest ... Calculating task graph as no cached configuration is available for tasks: someTask > Task :someTask FAILED 1 problem was found storing the configuration cache. - Build file 'build.gradle': line 6: invocation of 'Task.project' at execution time is unsupported with the configuration cache. See https://docs.gradle.org.cn/0.0.0/userguide/configuration_cache_requirements.html#config_cache:requirements:use_project_during_execution See the complete report at file:///home/user/gradle/samples/build/reports/configuration-cache/<hash>/configuration-cache-report.html 1 actionable task: 1 executed Configuration cache entry discarded with 1 problem. FAILURE: Build failed with an exception. * Where: Build file '/home/user/gradle/samples/build.gradle' line: 6 * What went wrong: Execution failed for task ':someTask'. > Invocation of 'Task.project' by task ':someTask' at execution time is unsupported with the configuration cache. * Try: > Run with --stacktrace option to get the stack trace. > Run with --info or --debug option to get more log output. > Run with --scan to generate a Build Scan (Powered by Develocity). > Get more help at https://help.gradle.org. BUILD FAILED in 0s Configuration Cache entry discarded with 1 problem.
由于检测到问题,Gradle 会丢弃配置缓存条目,阻止在未来的构建中重用。
链接的 HTML 报告提供了检测到的问题的详细信息:
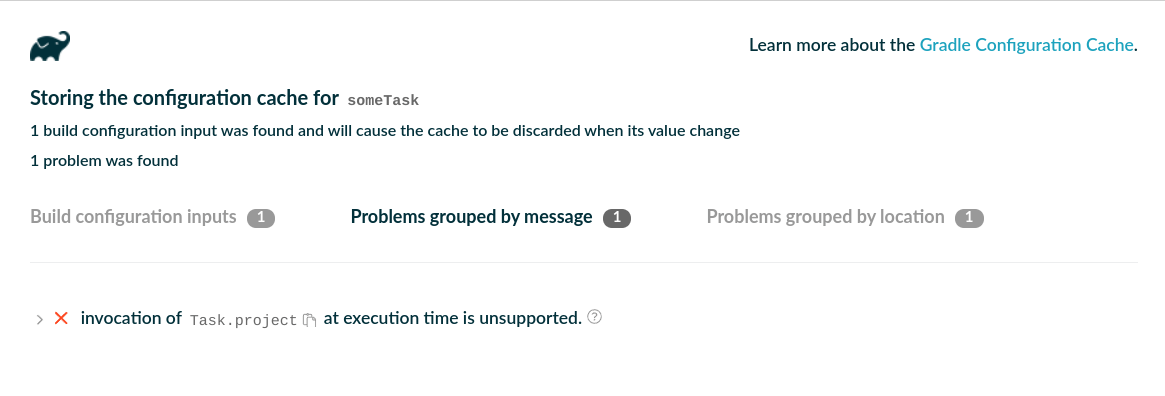
报告以两种方式呈现问题:
-
按消息分组 → 快速识别重复的问题类型。
-
按任务分组 → 识别哪些任务导致问题。
展开问题树有助于在对象图中找到根本原因。
此外,报告列出了检测到的构建配置输入,例如在配置期间访问的系统属性、环境变量和值供应商:
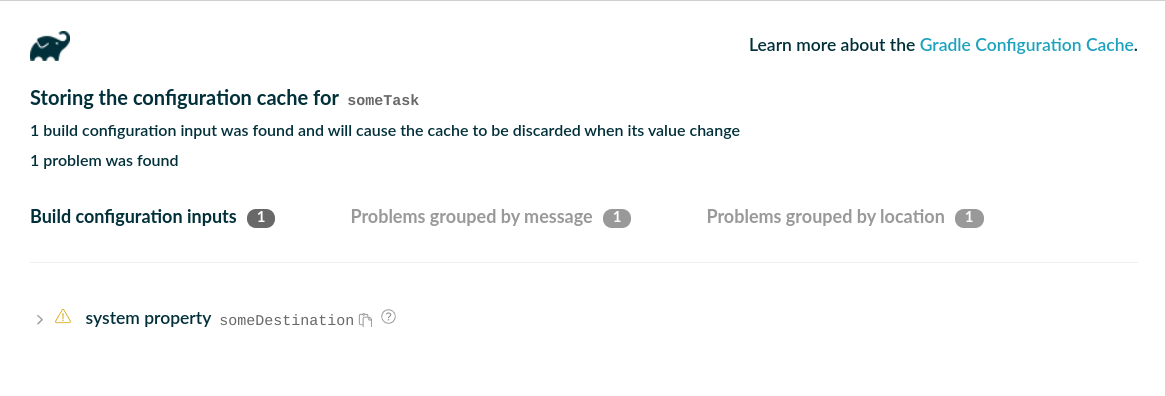
|
修改构建或插件时,考虑使用 TestKit 测试你的构建逻辑以验证更改。 |
在此阶段,你可以选择忽略问题(将其转换为警告)以继续探索配置缓存行为,或者立即修复问题。
要在观察问题的同时继续使用配置缓存,请运行:
❯ ./gradlew --configuration-cache --configuration-cache-problems=warn someTask -DsomeDestination=dest
Calculating task graph as no cached configuration is available for tasks: someTask
> Task :someTask
1 problem was found storing the configuration cache.
- Build file 'build.gradle': line 6: invocation of 'Task.project' at execution time is unsupported with the configuration cache.
See https://docs.gradle.org.cn/0.0.0/userguide/configuration_cache_requirements.html#config_cache:requirements:use_project_during_execution
See the complete report at file:///home/user/gradle/samples/build/reports/configuration-cache/<hash>/configuration-cache-report.html
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 0s
1 actionable task: 1 executed
Configuration Cache entry stored with 1 problem.
❯ ./gradlew --configuration-cache --configuration-cache-problems=warn someTask -DsomeDestination=dest
Reusing configuration cache.
> Task :someTask
1 problem was found reusing the configuration cache.
- Build file 'build.gradle': line 6: invocation of 'Task.project' at execution time is unsupported with the configuration cache.
See https://docs.gradle.org.cn/0.0.0/userguide/configuration_cache_requirements.html#config_cache:requirements:use_project_during_execution
See the complete report at file:///home/user/gradle/samples/build/reports/configuration-cache/<hash>/configuration-cache-report.html
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 0s
1 actionable task: 1 executed
Configuration Cache entry reused with 1 problem.Gradle 将成功存储和重用配置缓存,同时继续报告问题。
报告和控制台日志提供了指向解决检测到的问题的指导的链接。
这是示例构建脚本的修正版本:
abstract class MyCopyTask : DefaultTask() { (1)
@get:InputDirectory abstract val source: DirectoryProperty (2)
@get:OutputDirectory abstract val destination: DirectoryProperty (2)
@get:Inject abstract val fs: FileSystemOperations (3)
@TaskAction
fun action() {
fs.copy { (3)
from(source)
into(destination)
}
}
}
tasks.register<MyCopyTask>("someTask") {
val projectDir = layout.projectDirectory
source = projectDir.dir("source")
destination = projectDir.dir(System.getProperty("someDestination"))
}abstract class MyCopyTask extends DefaultTask { (1)
@InputDirectory abstract DirectoryProperty getSource() (2)
@OutputDirectory abstract DirectoryProperty getDestination() (2)
@Inject abstract FileSystemOperations getFs() (3)
@TaskAction
void action() {
fs.copy { (3)
from source
into destination
}
}
}
tasks.register('someTask', MyCopyTask) {
def projectDir = layout.projectDirectory
source = projectDir.dir('source')
destination = projectDir.dir(System.getProperty('someDestination'))
}| 1 | 我们将临时任务转换为一个适当的任务类, |
| 2 | 声明了输入和输出, |
| 3 | 并注入了 `FileSystemOperations` 服务,它是 `project.copy {}` 的受支持替代方案。 |
修复这些问题后,两次运行任务会成功重用配置缓存:
❯ ./gradlew --configuration-cache someTask -DsomeDestination=dest
Calculating task graph as no cached configuration is available for tasks: someTask
> Task :someTask
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 0s
1 actionable task: 1 executed
Configuration Cache entry stored.
❯ ./gradlew --configuration-cache someTask -DsomeDestination=dest
Reusing configuration cache.
> Task :someTask
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 0s
1 actionable task: 1 executed
Configuration Cache entry reused.如果构建输入发生变化(例如,系统属性值),配置缓存条目将失效,需要一个新的配置阶段:
❯ ./gradlew --configuration-cache someTask -DsomeDestination=another Calculating task graph as configuration cache cannot be reused because system property 'someDestination' has changed. > Task :someTask BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 0s 1 actionable task: 1 executed Configuration Cache entry stored.
缓存条目失效是因为在配置时读取了系统属性,当其值发生变化时,Gradle 会强制重新运行配置。
更好的方法是使用提供者将读取系统属性的时间推迟到执行时:
tasks.register<MyCopyTask>("someTask") {
val projectDir = layout.projectDirectory
source = projectDir.dir("source")
destination = projectDir.dir(providers.systemProperty("someDestination")) (1)
}tasks.register('someTask', MyCopyTask) {
def projectDir = layout.projectDirectory
source = projectDir.dir('source')
destination = projectDir.dir(providers.systemProperty('someDestination')) (1)
}| 1 | 我们直接连接了系统属性提供者,没有在配置时读取它。 |
现在,即使更改系统属性,缓存条目也仍然可重用:
❯ ./gradlew --configuration-cache someTask -DsomeDestination=dest Calculating task graph as no cached configuration is available for tasks: someTask > Task :someTask BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 0s 1 actionable task: 1 executed Configuration Cache entry stored. ❯ ./gradlew --configuration-cache someTask -DsomeDestination=another Reusing configuration cache. > Task :someTask BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 0s 1 actionable task: 1 executed Configuration Cache entry reused.
通过这些修复,此任务与配置缓存完全兼容。
启用警告模式
为了方便迁移,你可以将配置缓存问题视为警告而不是失败:
$ ./gradlew --configuration-cache-problems=warn或者在 `gradle.properties` 中设置:
org.gradle.configuration-cache.problems=warn|
警告模式是迁移和故障排除辅助工具,不应作为忽略不兼容性的长期方式。它也不会阻止以后意外地将新的不兼容性添加到构建中。 相反,我们建议明确将有问题任务标记为不兼容。 |
默认情况下,Gradle 允许最多 512 个警告,然后才会使构建失败。你可以降低此限制:
$ ./gradlew -Dorg.gradle.configuration-cache.max-problems=5声明不兼容任务
你可以使用 `Task.notCompatibleWithConfigurationCache()` 方法明确将任务标记为与配置缓存不兼容:
tasks.register("resolveAndLockAll") {
notCompatibleWithConfigurationCache("Filters configurations at execution time")
doFirst {
require(gradle.startParameter.isWriteDependencyLocks) { "$path must be run from the command line with the `--write-locks` flag" }
}
doLast {
configurations.filter {
// Add any custom filtering on the configurations to be resolved
it.isCanBeResolved
}.forEach { it.resolve() }
}
}tasks.register('resolveAndLockAll') {
notCompatibleWithConfigurationCache("Filters configurations at execution time")
doFirst {
assert gradle.startParameter.writeDependencyLocks : "$path must be run from the command line with the `--write-locks` flag"
}
doLast {
configurations.findAll {
// Add any custom filtering on the configurations to be resolved
it.canBeResolved
}.each { it.resolve() }
}
}当任务被标记为不兼容时,
-
该任务中的配置缓存问题将不再导致构建失败。
-
如果执行了不兼容的任务,Gradle 会在构建结束时丢弃配置状态。
此机制在迁移期间非常有用,允许你临时选择退出需要更广泛更改才能与配置缓存兼容的任务。
有关更多详细信息,请参阅方法文档。
使用完整性检查
为了减少条目大小并提高性能,Gradle 在写入和读取数据时执行最小的完整性检查。然而,这种方法会使故障排除变得更加困难,尤其是在处理并发问题或序列化错误时。不正确存储的对象可能无法立即检测到,但在稍后读取缓存数据时可能导致误导性或错误归因的错误。
为了简化调试,Gradle 提供了一个选项来启用更严格的完整性检查。此设置有助于更早地识别不一致性,但可能会减慢缓存操作并显著增加缓存条目大小。要启用更严格的完整性检查,请将以下行添加到你的 `gradle.properties` 文件中:
org.gradle.configuration-cache.integrity-check=true例如,让我们看一个错误实现自定义序列化协议的类型:
public class User implements Serializable {
private transient String name;
private transient int age;
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream out) throws IOException {
out.defaultWriteObject();
out.writeObject(name); (1)
out.writeInt(age);
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
in.defaultReadObject();
this.name = (String) in.readObject();
// this.age = in.readInt(); (2)
}
// ...| 1 | `writeObject` 序列化两个字段。 |
| 2 | `readObject` 只读取第一个字段,将剩余数据留在流中。 |
这样的类型在用作任务状态的一部分时会导致问题,因为配置缓存会尝试将对象中未读的剩余部分解释为一些新值:
public abstract class GreetTask extends DefaultTask {
User user = new User("John", 23);
@TaskAction
public void greet() {
System.out.println("Hello, " + user.getName() + "!");
System.out.println("Have a wonderful " + (user.getAge() + 1) +"th birthday!");
}
}在没有完整性检查的情况下运行时,你可能会遇到神秘的失败消息,可能伴随着诱发的配置缓存问题:
❯ gradle --configuration-cache greet ... * What went wrong: Index 4 out of bounds for length 3
这些错误可能不会立即指向根本原因,使调试更具挑战性。例如,将无效索引错误与序列化问题联系起来可能真的很难。
启用完整性检查后重新运行构建会提供更精确的诊断,帮助你更快地查明问题的来源:
❯ gradle --configuration-cache -Dorg.gradle.configuration-cache.integrity-check=true greet ... FAILURE: Build failed with an exception. * What went wrong: Configuration cache state could not be cached: field `user` of task `:greet` of type `GreetTask`: The value cannot be decoded properly with 'JavaObjectSerializationCodec'. It may have been written incorrectly or its data is corrupted.
你可以立即看到出错任务的名称以及包含损坏数据的字段。
请记住,这种归因是尽力而为的:在大多数情况下应该准确,但在极少数情况下,它可能会被某些字节模式混淆。
|
完整性检查依赖于存储在缓存中的额外元数据。因此,它不能用于诊断在启用完整性检查之前已经损坏的条目。 |
当前的完整性检查主要侧重于识别序列化协议问题,而不是一般的数据损坏。因此,它们对硬件相关问题(例如位腐烂或损坏的存储扇区)的效果较差。由于这些限制以及完整性检查引入的性能开销,我们建议选择性地将其作为故障排除措施启用,而不是永久启用。
检查缓存条目
Gradle 开发的 `gcc2speedscope` 工具通过将调试日志转换为与 speedscope.app 兼容的交互式火焰图来分析 Gradle 配置缓存的空间使用情况。
此可视化有助于识别缓存中大或不必要的对象。
调试配置阶段
`gradle-trace-converter` 是 Gradle 开发的命令行工具,用于分析和将构建操作跟踪转换为 Chrome 的 Perfetto 跟踪和 CSV 时间线等格式。
此可视化描绘了 Gradle 配置阶段期间执行的步骤。
测试你的构建逻辑
Gradle TestKit 是一个旨在促进测试 Gradle 插件和构建逻辑的库。有关使用 TestKit 的通用指南,请参阅专用章节。
要使用配置缓存启用测试你的构建逻辑,请将 `--configuration-cache` 参数传递给 `GradleRunner`,或使用启用配置缓存中描述的其他方法之一。
为了正确测试配置缓存行为,任务必须执行两次:
@Test
fun `my task can be loaded from the configuration cache`() {
buildFile.writeText("""
plugins {
id 'org.example.my-plugin'
}
""")
runner()
.withArguments("--configuration-cache", "myTask") (1)
.build()
val result = runner()
.withArguments("--configuration-cache", "myTask") (2)
.build()
require(result.output.contains("Reusing configuration cache.")) (3)
// ... more assertions on your task behavior
}def "my task can be loaded from the configuration cache"() {
given:
buildFile << """
plugins {
id 'org.example.my-plugin'
}
"""
when:
runner()
.withArguments('--configuration-cache', 'myTask') (1)
.build()
and:
def result = runner()
.withArguments('--configuration-cache', 'myTask') (2)
.build()
then:
result.output.contains('Reusing configuration cache.') (3)
// ... more assertions on your task behavior
}| 1 | 第一次运行预热配置缓存。 |
| 2 | 第二次运行重用配置缓存。 |
| 3 | 断言配置缓存被重用。 |
如果 Gradle 遇到配置缓存问题,它将使构建失败并报告问题,导致测试失败。
|
Gradle 插件作者推荐的方法是启用配置缓存运行整个测试套件。这确保了与受支持的 Gradle 版本的兼容性。
|