Gradle 能在一个项目上完成的工作由一个或多个任务定义。
一个任务代表构建执行的某个独立工作单元。这可能包括编译一些类、创建 JAR、生成 Javadoc 或将一些归档发布到仓库。
当用户在命令行中运行 ./gradlew build 时,Gradle 将执行 build 任务以及它所依赖的任何其他任务。
列出可用任务
Gradle 为项目提供了几个默认任务,可以通过运行 ./gradlew tasks 来列出。
> Task :tasks
------------------------------------------------------------
Tasks runnable from root project 'myTutorial'
------------------------------------------------------------
Build Setup tasks
-----------------
init - Initializes a new Gradle build.
wrapper - Generates Gradle wrapper files.
Help tasks
----------
buildEnvironment - Displays all buildscript dependencies declared in root project 'myTutorial'.
...任务要么来自构建脚本,要么来自插件。
一旦我们将插件应用到我们的项目,例如 application 插件,就会有额外的任务可用。
plugins {
id("application")
}plugins {
id 'application'
}$ ./gradlew tasks
> Task :tasks
------------------------------------------------------------
Tasks runnable from project ':app'
------------------------------------------------------------
Application tasks
-----------------
run - Runs this project as a JVM application
Build tasks
-----------
assemble - Assembles the outputs of this project.
build - Assembles and tests this project.
Documentation tasks
-------------------
javadoc - Generates Javadoc API documentation for the main source code.
Other tasks
-----------
compileJava - Compiles main Java source.
...其中许多任务,例如 assemble、build 和 run,应该对开发者来说很熟悉。
任务分类
有两种类型的任务可以执行
-
可操作任务 附加了一些动作以在您的构建中执行工作:
compileJava。 -
生命周期任务 是没有附加任何动作的任务:
assemble、build。
通常,生命周期任务 依赖于许多可操作任务,并用于一次性执行多个任务。
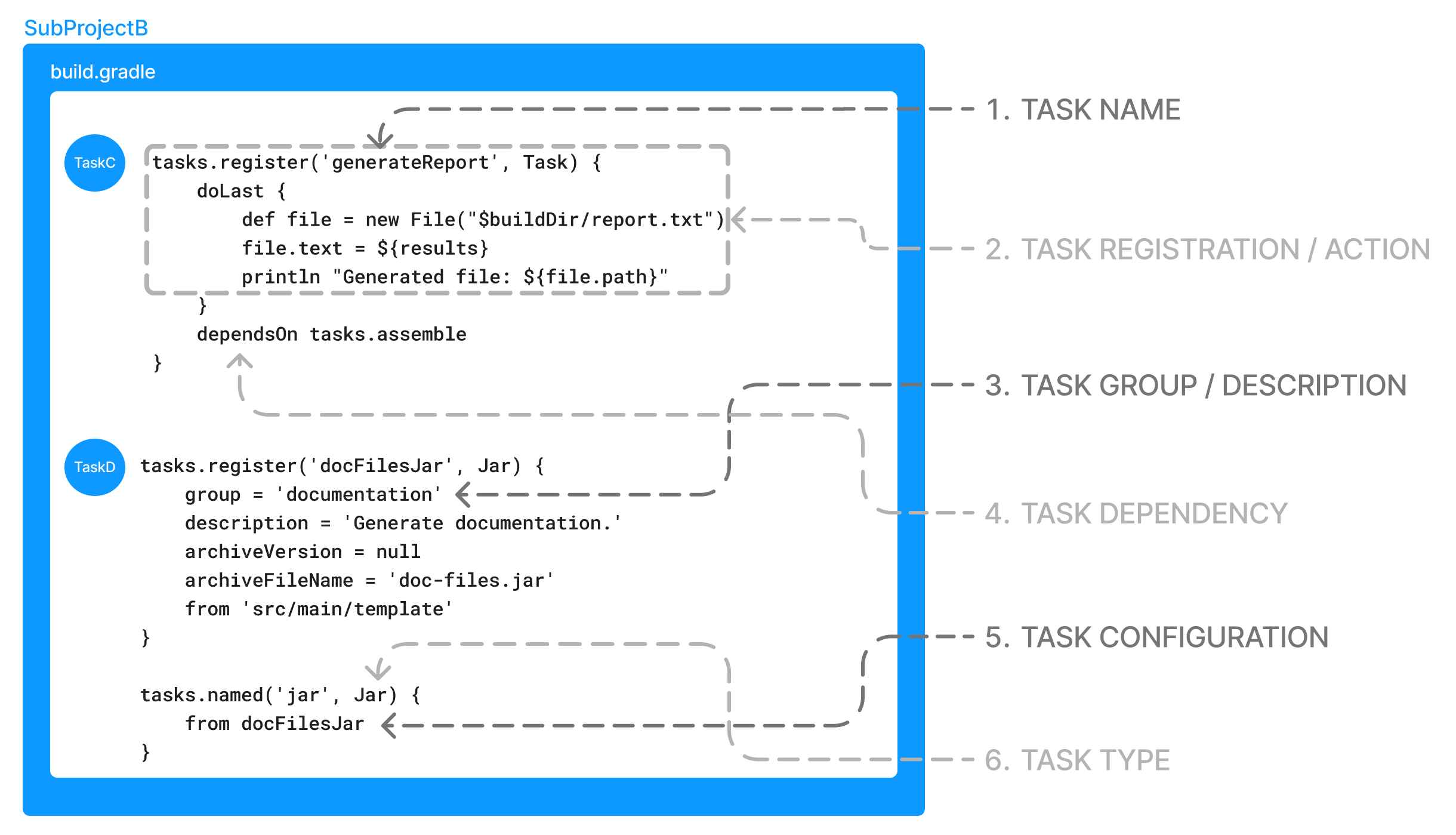
任务注册和动作
让我们来看一个简单的“Hello World”任务在构建脚本中
tasks.register("hello") {
doLast {
println("Hello world!")
}
}tasks.register('hello') {
doLast {
println 'Hello world!'
}
}在这个例子中,构建脚本使用 TaskContainer API注册了一个名为 hello 的单一任务,并为其添加了一个动作。
如果列出项目中的任务,hello 任务将对 Gradle 可用。
$ ./gradlew app:tasks --all
> Task :app:tasks
------------------------------------------------------------
Tasks runnable from project ':app'
------------------------------------------------------------
Other tasks
-----------
compileJava - Compiles main Java source.
compileTestJava - Compiles test Java source.
hello
processResources - Processes main resources.
processTestResources - Processes test resources.
startScripts - Creates OS-specific scripts to run the project as a JVM application.您可以使用 ./gradlew hello 在构建脚本中执行任务。
$ ./gradlew hello
Hello world!当 Gradle 执行 hello 任务时,它会执行所提供的动作。在这种情况下,动作只是一个包含一些代码的块:println("Hello world!")。
任务组和描述
前面章节的 hello 任务可以通过以下更新,使用描述进行详细说明,并分配给一个组。
tasks.register("hello") {
group = "Custom"
description = "A lovely greeting task."
doLast {
println("Hello world!")
}
}tasks.register('hello') {
group = 'Custom'
description = 'A lovely greeting task.'
doLast {
println 'Hello world!'
}
}一旦任务被分配到一个组,它将由 ./gradlew tasks 列出。
$ ./gradlew tasks
> Task :tasks
Custom tasks
------------------
hello - A lovely greeting task.要查看有关任务的信息,请使用 help --task <task-name> 命令。
$./gradlew help --task hello
> Task :help
Detailed task information for hello
Path
:app:hello
Type
Task (org.gradle.api.Task)
Options
--rerun Causes the task to be re-run even if up-to-date.
Description
A lovely greeting task.
Group
Custom正如我们所看到的,hello 任务属于 custom 组。
任务依赖
您可以声明依赖于其他任务的任务。
tasks.register("hello") {
doLast {
println("Hello world!")
}
}
tasks.register("intro") {
dependsOn("hello")
doLast {
println("I'm Gradle")
}
}tasks.register('hello') {
doLast {
println 'Hello world!'
}
}
tasks.register('intro') {
dependsOn tasks.hello
doLast {
println "I'm Gradle"
}
}$ gradle -q intro Hello world! I'm Gradle
taskX 对 taskY 的依赖可以在 taskY 定义之前声明。
tasks.register("taskX") {
dependsOn("taskY")
doLast {
println("taskX")
}
}
tasks.register("taskY") {
doLast {
println("taskY")
}
}tasks.register('taskX') {
dependsOn 'taskY'
doLast {
println 'taskX'
}
}
tasks.register('taskY') {
doLast {
println 'taskY'
}
}$ gradle -q taskX taskY taskX
前面的例子中的 hello 任务更新为包含一个依赖项
tasks.register("hello") {
group = "Custom"
description = "A lovely greeting task."
doLast {
println("Hello world!")
}
dependsOn(tasks.assemble)
}tasks.register('hello') {
group = "Custom"
description = "A lovely greeting task."
doLast {
println("Hello world!")
}
dependsOn(tasks.assemble)
}hello 任务现在依赖于 assemble 任务,这意味着 Gradle 必须在执行 hello 任务之前执行 assemble 任务。
$ ./gradlew :app:hello
> Task :app:compileJava UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:processResources NO-SOURCE
> Task :app:classes UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:jar UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:startScripts UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:distTar UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:distZip UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:assemble UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:hello
Hello world!任务配置
注册后,任务可以通过 TaskProvider API 访问以进行进一步配置。
例如,您可以使用它在运行时动态地向任务添加依赖项。
repeat(4) { counter ->
tasks.register("task$counter") {
doLast {
println("I'm task number $counter")
}
}
}
tasks.named("task0") { dependsOn("task2", "task3") }4.times { counter ->
tasks.register("task$counter") {
doLast {
println "I'm task number $counter"
}
}
}
tasks.named('task0') { dependsOn('task2', 'task3') }$ gradle -q task0 I'm task number 2 I'm task number 3 I'm task number 0
或者您可以向现有任务添加行为
tasks.register("hello") {
doLast {
println("Hello Earth")
}
}
tasks.named("hello") {
doFirst {
println("Hello Venus")
}
}
tasks.named("hello") {
doLast {
println("Hello Mars")
}
}
tasks.named("hello") {
doLast {
println("Hello Jupiter")
}
}tasks.register('hello') {
doLast {
println 'Hello Earth'
}
}
tasks.named('hello') {
doFirst {
println 'Hello Venus'
}
}
tasks.named('hello') {
doLast {
println 'Hello Mars'
}
}
tasks.named('hello') {
doLast {
println 'Hello Jupiter'
}
}$ gradle -q hello Hello Venus Hello Earth Hello Mars Hello Jupiter
doFirst 和 doLast 调用可以多次执行。它们向任务的动作列表的开头或结尾添加一个动作。当任务执行时,动作列表中的动作按顺序执行。 |
以下是使用 named 方法配置由插件添加的任务的示例
tasks.dokkaHtml.configure {
outputDirectory.set(buildDir)
}tasks.named("dokkaHtml") {
outputDirectory.set(buildDir)
}任务类型
Gradle 任务是 Task 的子类。
在构建脚本中,HelloTask 类通过扩展 DefaultTask 创建。
// Extend the DefaultTask class to create a HelloTask class
abstract class HelloTask : DefaultTask() {
@TaskAction
fun hello() {
println("hello from HelloTask")
}
}
// Register the hello Task with type HelloTask
tasks.register<HelloTask>("hello") {
group = "Custom tasks"
description = "A lovely greeting task."
}// Extend the DefaultTask class to create a HelloTask class
class HelloTask extends DefaultTask {
@TaskAction
void hello() {
println("hello from HelloTask")
}
}
// Register the hello Task with type HelloTask
tasks.register("hello", HelloTask) {
group = "Custom tasks"
description = "A lovely greeting task."
}hello 任务以 HelloTask 类型注册。
执行我们的新 hello 任务
$ ./gradlew hello
> Task :app:hello
hello from HelloTask现在 hello 任务的类型是 HelloTask 而不是 Task。
Gradle 的 help 任务揭示了这一变化。
$ ./gradlew help --task hello
> Task :help
Detailed task information for hello
Path
:app:hello
Type
HelloTask (Build_gradle$HelloTask)
Options
--rerun Causes the task to be re-run even if up-to-date.
Description
A lovely greeting task.
Group
Custom tasks内置任务类型
Gradle 提供了许多内置任务类型,具有常用和流行的功能,例如复制或删除文件。
这个示例任务使用 Copy 内置任务将 *.war 文件从 source 目录复制到 target 目录。
tasks.register<Copy>("copyTask") {
from("source")
into("target")
include("*.war")
}tasks.register('copyTask', Copy) {
from("source")
into("target")
include("*.war")
}开发人员可以利用许多任务类型,包括 GroovyDoc、Zip、Jar、JacocoReport、Sign 或 Delete,这些都可以在 DSL 中找到。
下一步: 学习如何编写任务 >>