在 Gradle 中声明依赖项涉及指定项目所依赖的库或文件。
了解生产者和消费者
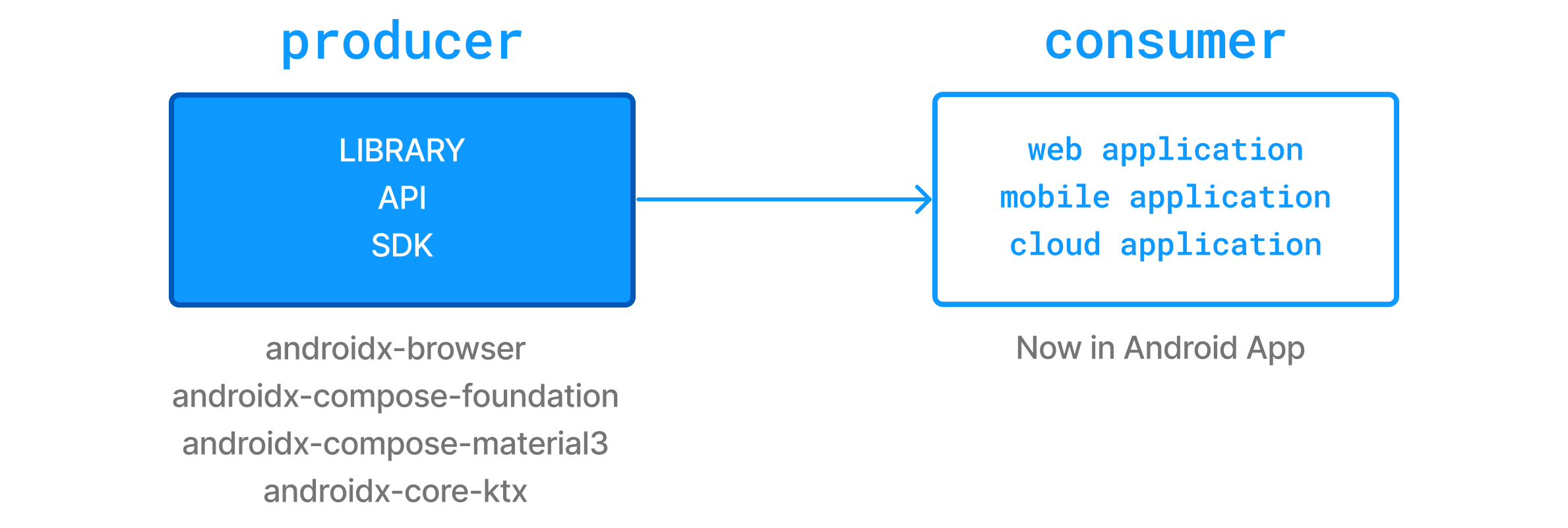
在依赖项管理中,理解“生产者”和“消费者”之间的区别至关重要。
当你构建一个库时,你扮演着“生产者”的角色,创建将供他人(“消费者”)使用的工件。
当你依赖该库时,你扮演着“消费者”的角色。“消费者”可以 broadly 定义为:
-
依赖其他项目的项目。
-
声明对特定工件的依赖的配置。
我们在依赖项管理中做出的决策通常取决于我们正在构建的项目类型,特别是我们是什么样的“消费者”。
添加依赖项
要在 Gradle 中添加依赖项,请在构建脚本中使用 dependencies{} 块。
dependencies 块允许你指定各种类型的依赖项,例如外部库、本地 JAR 文件或多项目构建中的其他项目。
Gradle 中的外部依赖项使用配置名称(例如 implementation、compileOnly、testImplementation)声明,后跟依赖项符号,其中包括组 ID (group)、工件 ID (name) 和版本。
dependencies {
// Configuration Name + Dependency Notation - GroupID : ArtifactID (Name) : Version
configuration('<group>:<name>:<version>')
}注意
了解依赖项类型
依赖项有三种:模块依赖项、项目依赖项和文件依赖项。
1. 模块依赖项
模块依赖项是最常见的依赖项。它们指的是仓库中的一个模块。
dependencies {
implementation("org.codehaus.groovy:groovy:3.0.5")
implementation("org.codehaus.groovy:groovy-json:3.0.5")
implementation("org.codehaus.groovy:groovy-nio:3.0.5")
}dependencies {
implementation 'org.codehaus.groovy:groovy:3.0.5'
implementation 'org.codehaus.groovy:groovy-json:3.0.5'
implementation 'org.codehaus.groovy:groovy-nio:3.0.5'
}2. 项目依赖项
项目依赖项允许你声明对同一构建中其他项目的依赖。这在多项目构建中非常有用,其中多个项目是同一 Gradle 构建的一部分。
项目依赖项通过引用项目路径来声明。
dependencies {
implementation(project(":utils"))
implementation(project(":api"))
}dependencies {
implementation project(':utils')
implementation project(':api')
}3. 文件依赖项
在某些项目中,你可能不依赖像 JFrog Artifactory 或 Sonatype Nexus 这样的二进制仓库产品来托管和解析外部依赖项。相反,你可能会在共享驱动器上托管这些依赖项,或者将它们与项目源代码一起检入版本控制。
这些被称为文件依赖项,因为它们表示没有任何元数据(例如有关传递性依赖项、来源或作者的信息)附加的文件。
要将文件添加为配置的依赖项,你只需将文件集合作为依赖项传递。
dependencies {
runtimeOnly(files("libs/a.jar", "libs/b.jar"))
runtimeOnly(fileTree("libs") { include("*.jar") })
}dependencies {
runtimeOnly files('libs/a.jar', 'libs/b.jar')
runtimeOnly fileTree('libs') { include '*.jar' }
}| 建议使用项目依赖项或外部依赖项,而不是文件依赖项。 |
查看示例
让我们想象一个 Java 应用程序的示例,它使用 Guava,一组来自 Google 的核心 Java 库。
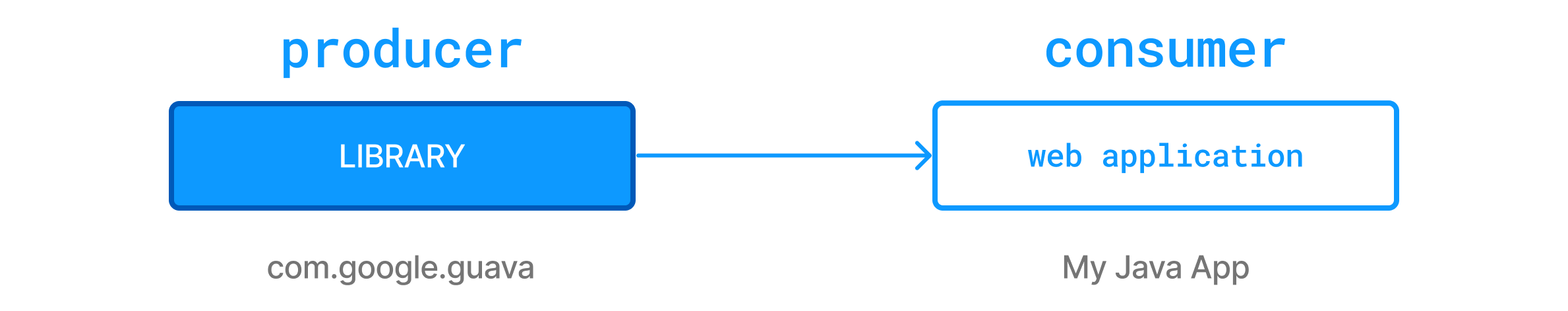
Java 应用程序包含以下 Java 类:
package org.example;
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableMap; // Comes from the Guava library
public class InitializeCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImmutableMap<String, Integer> immutableMap
= ImmutableMap.of("coin", 3, "glass", 4, "pencil", 1);
}
}要将 Guava 库作为依赖项添加到你的 Gradle 项目中,你必须将以下行添加到构建文件中:
dependencies {
implementation("com.google.guava:guava:23.0")
}dependencies {
implementation 'com.google.guava:guava:23.0'
}其中
-
implementation是配置。 -
com.google.guava:guava:23.0指定库的组、名称和版本。-
com.google.guava是组 ID。 -
guava是工件 ID(即名称)。 -
23.0是版本。
-
快速查看 Maven Central 中的 Guava 页面作为参考。
列出项目依赖项
dependencies 任务提供了项目依赖项的概述。它通过从命令行渲染依赖项树,帮助你了解正在使用哪些依赖项、它们如何解析以及它们的关系,包括任何传递性依赖项。
此任务对于调试依赖项问题(例如版本冲突或缺少依赖项)特别有用。
例如,假设我们的 app 项目在构建脚本中包含以下行:
dependencies {
implementation("com.google.guava:guava:30.0-jre")
runtimeOnly("org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.14.0")
}dependencies {
implementation("com.google.guava:guava:30.0-jre")
runtimeOnly("org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.14.0")
}对 app 项目运行 dependencies 任务会得到以下结果:
$ ./gradlew app:dependencies > Task :app:dependencies ------------------------------------------------------------ Project ':app' ------------------------------------------------------------ implementation - Implementation dependencies for the 'main' feature. (n) \--- com.google.guava:guava:30.0-jre (n) runtimeClasspath - Runtime classpath of source set 'main'. +--- com.google.guava:guava:30.0-jre | +--- com.google.guava:failureaccess:1.0.1 | +--- com.google.guava:listenablefuture:9999.0-empty-to-avoid-conflict-with-guava | +--- com.google.code.findbugs:jsr305:3.0.2 | +--- org.checkerframework:checker-qual:3.5.0 | +--- com.google.errorprone:error_prone_annotations:2.3.4 | \--- com.google.j2objc:j2objc-annotations:1.3 \--- org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.14.0 runtimeOnly - Runtime-only dependencies for the 'main' feature. (n) \--- org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.14.0 (n)
我们可以清楚地看到,对于 implementation 配置,已添加 com.google.guava:guava:30.0-jre 依赖项。对于 runtimeOnly 配置,已添加 org.org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.14.0 依赖项。
我们还看到了 com.google.guava:guava:30.0-jre 的传递性依赖项列表(它们是 guava 库的依赖项),例如 runtimeClasspath 配置中的 com.google.guava:failureaccess:1.0.1。
下一步: 了解依赖项配置 >>