列出任务
项目中所有可用任务都来自 Gradle 插件和构建脚本。
您可以通过在终端中运行以下命令来列出项目中所有可用任务:
$ ./gradlew tasks让我们以一个非常基本的 Gradle 项目为例。该项目具有以下结构:
gradle-project
├── app
│ ├── build.gradle.kts // empty file - no build logic
│ └── ... // some java code
├── settings.gradle.kts // includes app subproject
├── gradle
│ └── ...
├── gradlew
└── gradlew.batgradle-project
├── app
│ ├── build.gradle // empty file - no build logic
│ └── ... // some java code
├── settings.gradle // includes app subproject
├── gradle
│ └── ...
├── gradlew
└── gradlew.batsettings 文件包含以下内容:
rootProject.name = "gradle-project"
include("app")rootProject.name = 'gradle-project'
include('app')目前,app 子项目的构建文件为空。
要查看 app 子项目中可用的任务,请运行 ./gradlew :app:tasks
$ ./gradlew :app:tasks
> Task :app:tasks
------------------------------------------------------------
Tasks runnable from project ':app'
------------------------------------------------------------
Help tasks
----------
buildEnvironment - Displays all buildscript dependencies declared in project ':app'.
dependencies - Displays all dependencies declared in project ':app'.
dependencyInsight - Displays the insight into a specific dependency in project ':app'.
help - Displays a help message.
javaToolchains - Displays the detected java toolchains.
kotlinDslAccessorsReport - Prints the Kotlin code for accessing the currently available project extensions and conventions.
outgoingVariants - Displays the outgoing variants of project ':app'.
projects - Displays the sub-projects of project ':app'.
properties - Displays the properties of project ':app'.
resolvableConfigurations - Displays the configurations that can be resolved in project ':app'.
tasks - Displays the tasks runnable from project ':app'.我们发现目前只有少量帮助任务可用。这是因为 Gradle 核心只提供分析构建的任务。其他任务,例如构建项目或编译代码的任务,是由插件添加的。
让我们通过向 app 构建脚本添加 Gradle 核心 base 插件来探索这一点:
plugins {
id("base")
}plugins {
id('base')
}base 插件添加了核心生命周期任务。现在当我们运行 ./gradlew app:tasks 时,我们可以看到 assemble 和 build 任务可用。
$ ./gradlew :app:tasks
> Task :app:tasks
------------------------------------------------------------
Tasks runnable from project ':app'
------------------------------------------------------------
Build tasks
-----------
assemble - Assembles the outputs of this project.
build - Assembles and tests this project.
clean - Deletes the build directory.
Help tasks
----------
buildEnvironment - Displays all buildscript dependencies declared in project ':app'.
dependencies - Displays all dependencies declared in project ':app'.
dependencyInsight - Displays the insight into a specific dependency in project ':app'.
help - Displays a help message.
javaToolchains - Displays the detected java toolchains.
outgoingVariants - Displays the outgoing variants of project ':app'.
projects - Displays the sub-projects of project ':app'.
properties - Displays the properties of project ':app'.
resolvableConfigurations - Displays the configurations that can be resolved in project ':app'.
tasks - Displays the tasks runnable from project ':app'.
Verification tasks
------------------
check - Runs all checks.任务结果
当 Gradle 执行任务时,它会通过控制台为任务标记结果。
这些标签基于任务是否有要执行的操作以及 Gradle 是否执行了这些操作。操作包括但不限于编译代码、压缩文件和发布归档。
任务组和描述
任务组和描述用于组织和描述任务。
- 组
-
任务组用于对任务进行分类。当您运行
./gradlew tasks时,任务会列在其各自的组下,从而更容易理解其目的以及与其他任务的关系。组使用group属性设置。 - 描述
-
描述提供任务功能的简要说明。当您运行
./gradlew tasks时,描述会显示在每个任务旁边,帮助您了解其目的和用法。描述使用description属性设置。
让我们以一个基本的 Java 应用程序为例。构建包含一个名为 app 的子项目。
让我们现在列出 app 中可用的任务:
$ ./gradlew :app:tasks
> Task :app:tasks
------------------------------------------------------------
Tasks runnable from project ':app'
------------------------------------------------------------
Application tasks
-----------------
run - Runs this project as a JVM application.
Build tasks
-----------
assemble - Assembles the outputs of this project.这里,:run 任务属于 Application 组,描述为 Runs this project as a JVM application。在代码中,它看起来像这样:
tasks.register("run") {
group = "Application"
description = "Runs this project as a JVM application."
}tasks.register("run") {
group = "Application"
description = "Runs this project as a JVM application."
}私有和隐藏任务
Gradle 不支持将任务标记为私有。
但是,只有当 task.group 被设置或没有其他任务依赖它时,任务才会显示在运行 :tasks 时。
例如,以下任务在运行 ./gradlew :app:tasks 时不会出现,因为它没有组;它被称为隐藏任务。
tasks.register("helloTask") {
println("Hello")
}tasks.register("helloTask") {
println 'Hello'
}尽管 helloTask 未列出,但它仍然可以由 Gradle 执行。
$ ./gradlew :app:tasks
> Task :app:tasks
------------------------------------------------------------
Tasks runnable from project ':app'
------------------------------------------------------------
Application tasks
-----------------
run - Runs this project as a JVM application
Build tasks
-----------
assemble - Assembles the outputs of this project.让我们为同一个任务添加一个组:
tasks.register("helloTask") {
group = "Other"
description = "Hello task"
println("Hello")
}tasks.register("helloTask") {
group = "Other"
description = "Hello task"
println 'Hello'
}现在添加了组,任务可见:
$ ./gradlew :app:tasks
> Task :app:tasks
------------------------------------------------------------
Tasks runnable from project ':app'
------------------------------------------------------------
Application tasks
-----------------
run - Runs this project as a JVM application
Build tasks
-----------
assemble - Assembles the outputs of this project.
Other tasks
-----------
helloTask - Hello task相反,./gradlew tasks --all 将显示所有任务;隐藏和可见任务都会列出。
任务分组
如果您想自定义列出任务时向用户显示哪些任务,您可以对任务进行分组并设置每个组的可见性。
| 请记住,即使您隐藏了任务,它们仍然可用,并且 Gradle 仍然可以运行它们。 |
让我们从一个由 Gradle init 为具有多个子项目的 Java 应用程序构建的示例开始。项目结构如下:
gradle-project
├── app
│ ├── build.gradle.kts
│ └── src // some java code
│ └── ...
├── utilities
│ ├── build.gradle.kts
│ └── src // some java code
│ └── ...
├── list
│ ├── build.gradle.kts
│ └── src // some java code
│ └── ...
├── buildSrc
│ ├── build.gradle.kts
│ ├── settings.gradle.kts
│ └── src // common build logic
│ └── ...
├── settings.gradle.kts
├── gradle
├── gradlew
└── gradlew.batgradle-project
├── app
│ ├── build.gradle
│ └── src // some java code
│ └── ...
├── utilities
│ ├── build.gradle
│ └── src // some java code
│ └── ...
├── list
│ ├── build.gradle
│ └── src // some java code
│ └── ...
├── buildSrc
│ ├── build.gradle
│ ├── settings.gradle
│ └── src // common build logic
│ └── ...
├── settings.gradle
├── gradle
├── gradlew
└── gradlew.bat运行 app:tasks 以查看 app 子项目中可用的任务:
$ ./gradlew :app:tasks
> Task :app:tasks
------------------------------------------------------------
Tasks runnable from project ':app'
------------------------------------------------------------
Application tasks
-----------------
run - Runs this project as a JVM application
Build tasks
-----------
assemble - Assembles the outputs of this project.
build - Assembles and tests this project.
buildDependents - Assembles and tests this project and all projects that depend on it.
buildNeeded - Assembles and tests this project and all projects it depends on.
classes - Assembles main classes.
clean - Deletes the build directory.
jar - Assembles a jar archive containing the classes of the 'main' feature.
testClasses - Assembles test classes.
Distribution tasks
------------------
assembleDist - Assembles the main distributions
distTar - Bundles the project as a distribution.
distZip - Bundles the project as a distribution.
installDist - Installs the project as a distribution as-is.
Documentation tasks
-------------------
javadoc - Generates Javadoc API documentation for the 'main' feature.
Help tasks
----------
buildEnvironment - Displays all buildscript dependencies declared in project ':app'.
dependencies - Displays all dependencies declared in project ':app'.
dependencyInsight - Displays the insight into a specific dependency in project ':app'.
help - Displays a help message.
javaToolchains - Displays the detected java toolchains.
kotlinDslAccessorsReport - Prints the Kotlin code for accessing the currently available project extensions and conventions.
outgoingVariants - Displays the outgoing variants of project ':app'.
projects - Displays the sub-projects of project ':app'.
properties - Displays the properties of project ':app'.
resolvableConfigurations - Displays the configurations that can be resolved in project ':app'.
tasks - Displays the tasks runnable from project ':app'.
Verification tasks
------------------
check - Runs all checks.
test - Runs the test suite.如果我们查看可用任务列表,即使对于标准 Java 项目,它也是非常庞大的。其中许多任务很少被使用构建的开发人员直接需要。
我们可以配置 :tasks 任务并限制显示特定组的任务。
让我们创建自己的组,以便通过更新 app 构建脚本来默认隐藏所有任务:
val myBuildGroup = "my app build" // Create a group name
tasks.register<TaskReportTask>("tasksAll") { // Register the tasksAll task
group = myBuildGroup
description = "Show additional tasks."
setShowDetail(true)
}
tasks.named<TaskReportTask>("tasks") { // Move all existing tasks to the group
displayGroup = myBuildGroup
}def myBuildGroup = "my app build" // Create a group name
tasks.register("tasksAll", TaskReportTask) { // Register the tasksAll task
group = myBuildGroup
description = "Show additional tasks."
setShowDetail(true)
}
tasks.named("tasks", TaskReportTask) { // Move all existing tasks to the group
displayGroup = myBuildGroup
}现在,当我们列出 app 中可用的任务时,列表更短了:
$ ./gradlew :app:tasks
> Task :app:tasks
------------------------------------------------------------
Tasks runnable from project ':app'
------------------------------------------------------------
My app build tasks
------------------
tasksAll - Show additional tasks.任务类别
Gradle 区分两种任务类别:
-
生命周期任务
-
可执行任务
生命周期任务定义您可以调用的目标,例如 :build 您的项目。生命周期任务不为 Gradle 提供操作。它们必须连接到可执行任务。base Gradle 插件只添加生命周期任务。
可执行任务定义 Gradle 要执行的操作,例如 :compileJava,它编译项目的 Java 代码。操作包括创建 JAR、压缩文件、发布归档等等。像java-library 插件这样的插件会添加可执行任务。
让我们更新上一个示例的构建脚本,它目前是一个空文件,以便我们的 app 子项目成为 Java 库:
plugins {
id("java-library")
}plugins {
id('java-library')
}我们再次列出可用任务,看看有哪些新任务可用:
$ ./gradlew :app:tasks
> Task :app:tasks
------------------------------------------------------------
Tasks runnable from project ':app'
------------------------------------------------------------
Build tasks
-----------
assemble - Assembles the outputs of this project.
build - Assembles and tests this project.
buildDependents - Assembles and tests this project and all projects that depend on it.
buildNeeded - Assembles and tests this project and all projects it depends on.
classes - Assembles main classes.
clean - Deletes the build directory.
jar - Assembles a jar archive containing the classes of the 'main' feature.
testClasses - Assembles test classes.
Documentation tasks
-------------------
javadoc - Generates Javadoc API documentation for the 'main' feature.
Help tasks
----------
buildEnvironment - Displays all buildscript dependencies declared in project ':app'.
dependencies - Displays all dependencies declared in project ':app'.
dependencyInsight - Displays the insight into a specific dependency in project ':app'.
help - Displays a help message.
javaToolchains - Displays the detected java toolchains.
outgoingVariants - Displays the outgoing variants of project ':app'.
projects - Displays the sub-projects of project ':app'.
properties - Displays the properties of project ':app'.
resolvableConfigurations - Displays the configurations that can be resolved in project ':app'.
tasks - Displays the tasks runnable from project ':app'.
Verification tasks
------------------
check - Runs all checks.
test - Runs the test suite.我们看到许多新任务可用,例如 jar 和 testClasses。
此外,java-library 插件已将可执行任务连接到生命周期任务。如果我们调用 :build 任务,我们可以看到几个任务已执行,包括 :app:compileJava 任务。
$./gradlew :app:build
> Task :app:compileJava
> Task :app:processResources NO-SOURCE
> Task :app:classes
> Task :app:jar
> Task :app:assemble
> Task :app:compileTestJava
> Task :app:processTestResources NO-SOURCE
> Task :app:testClasses
> Task :app:test
> Task :app:check
> Task :app:build可执行的 :compileJava 任务连接到生命周期的 :build 任务。
增量任务
Gradle 任务的一个关键特性是它们的增量性质。
Gradle 可以重用先前构建的结果。因此,如果我们之前构建过项目并且只进行了少量更改,重新运行 :build 将不需要 Gradle 执行大量工作。
例如,如果我们在项目中只修改了测试代码,而生产代码保持不变,执行构建将只重新编译测试代码。Gradle 将生产代码的任务标记为 UP-TO-DATE,表明自上次成功构建以来它保持不变。
$./gradlew :app:build
gradle@MacBook-Pro temp1 % ./gradlew :app:build
> Task :app:compileJava UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:processResources NO-SOURCE
> Task :app:classes UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:jar UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:assemble UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:compileTestJava
> Task :app:processTestResources NO-SOURCE
> Task :app:testClasses
> Task :app:test
> Task :app:check UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:build UP-TO-DATE缓存任务
Gradle 可以使用构建缓存重用过去构建的结果。
要启用此功能,请使用 --build-cache 命令行参数激活构建缓存,或者在您的 gradle.properties 文件中设置 org.gradle.caching=true。
此优化有可能显著加快您的构建速度。
$./gradlew :app:clean :app:build --build-cache
> Task :app:compileJava FROM-CACHE
> Task :app:processResources NO-SOURCE
> Task :app:classes UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:jar
> Task :app:assemble
> Task :app:compileTestJava FROM-CACHE
> Task :app:processTestResources NO-SOURCE
> Task :app:testClasses UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:test FROM-CACHE
> Task :app:check UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:build当 Gradle 可以从缓存中获取任务的输出时,它会用 FROM-CACHE 标记该任务。
如果您经常切换分支,构建缓存会很有用。Gradle 支持本地和远程构建缓存。
开发任务
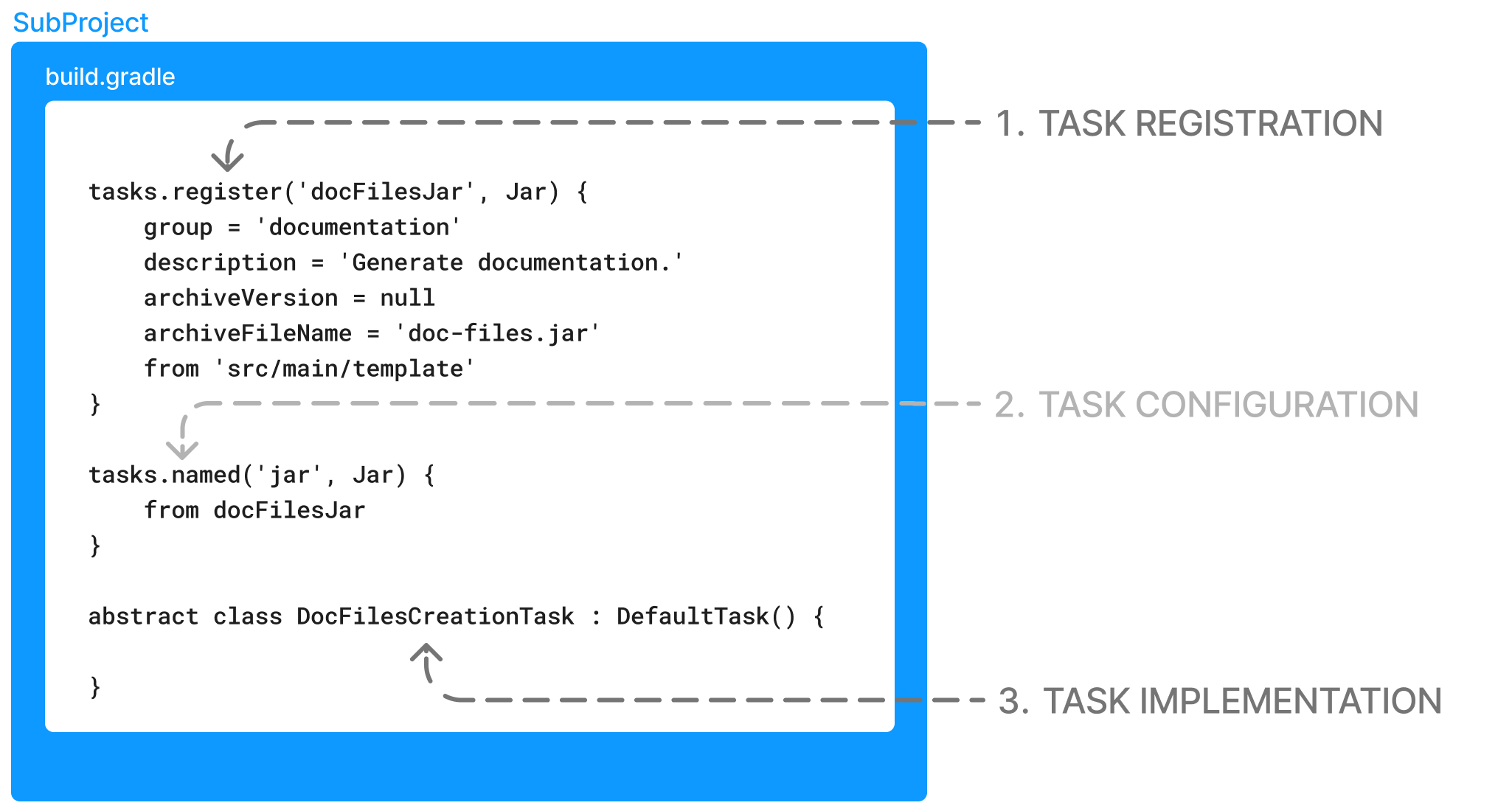
开发 Gradle 任务时,您有两种选择:
-
使用现有的 Gradle 任务类型,例如
Zip、Copy或Delete。 -
创建自己的 Gradle 任务类型,例如
MyResolveTask或CustomTaskUsingToolchains。
任务类型只是 Gradle Task 类的子类。
对于 Gradle 任务,有三种状态需要考虑:
-
注册任务 - 在构建逻辑中使用任务(由您实现或由 Gradle 提供)。
-
配置任务 - 为已注册任务定义输入和输出。
-
实现任务 - 创建自定义任务类(即,自定义类类型)。
注册通常使用 register() 方法完成。
配置任务通常使用 named() 方法完成。
实现任务通常通过扩展 Gradle 的 DefaultTask 类来完成:
tasks.register<Copy>("myCopy") (1)
tasks.named<Copy>("myCopy") { (2)
from("resources")
into("target")
include("**/*.txt", "**/*.xml", "**/*.properties")
}
abstract class MyCopyTask : DefaultTask() { (3)
@TaskAction
fun copyFiles() {
val sourceDir = File("sourceDir")
val destinationDir = File("destinationDir")
sourceDir.listFiles()?.forEach { file ->
if (file.isFile && file.extension == "txt") {
file.copyTo(File(destinationDir, file.name))
}
}
}
}| 1 | 注册 Copy 类型的 myCopy 任务,让 Gradle 知道我们打算在构建逻辑中使用它。 |
| 2 | 根据其 API,配置已注册的 myCopy 任务所需的输入和输出。 |
| 3 | 实现一个名为 MyCopyTask 的自定义任务类型,它扩展 DefaultTask 并定义 copyFiles 任务操作。 |
tasks.register("myCopy", Copy) (1)
tasks.named("myCopy", Copy) { (2)
from "resources"
into "target"
include "**/*.txt", "**/*.xml", "**/*.properties"
}
abstract class MyCopyTask extends DefaultTask { (3)
@TaskAction
void copyFiles() {
fileTree('sourceDir').matching {
include '**/*.txt'
}.forEach { file ->
file.copyTo(file.path.replace('sourceDir', 'destinationDir'))
}
}
}| 1 | 注册 Copy 类型的 myCopy 任务,让 Gradle 知道我们打算在构建逻辑中使用它。 |
| 2 | 根据其 API,配置已注册的 myCopy 任务所需的输入和输出。 |
| 3 | 实现一个名为 MyCopyTask 的自定义任务类型,它扩展 DefaultTask 并定义 copyFiles 任务操作。 |
1. 注册任务
您通过在构建脚本或插件中注册任务来定义 Gradle 要执行的操作。
任务使用字符串作为任务名称来定义。
tasks.register("hello") {
doLast {
println("hello")
}
}tasks.register('hello') {
doLast {
println 'hello'
}
}在上面的示例中,任务通过 TaskContainer 中的 register() 方法添加到 TasksCollection。
2. 配置任务
Gradle 任务必须经过配置才能成功完成其操作。如果任务需要压缩文件,则必须配置文件名和位置。您可以参考 Gradle Zip 任务的 API 来了解如何正确配置它。
让我们以 Gradle 提供的 Copy 任务为例。我们首先在构建脚本中注册一个 Copy 类型的任务 myCopy:
tasks.register<Copy>("myCopy")tasks.register('myCopy', Copy)这将注册一个没有默认行为的复制任务。由于任务是 Copy 类型,一种 Gradle 支持的任务类型,因此可以使用其 API 进行配置。
以下示例显示了几种实现相同配置的方法:
1. 使用 named() 方法:
使用 named() 配置在其他地方注册的现有任务。
tasks.named<Copy>("myCopy") {
from("resources")
into("target")
include("**/*.txt", "**/*.xml", "**/*.properties")
}tasks.named('myCopy') {
from 'resources'
into 'target'
include('**/*.txt', '**/*.xml', '**/*.properties')
}2. 使用配置块:
使用块在注册任务后立即配置任务。
tasks.register<Copy>("copy") {
from("resources")
into("target")
include("**/*.txt", "**/*.xml", "**/*.properties")
}tasks.register('copy', Copy) {
from 'resources'
into 'target'
include('**/*.txt', '**/*.xml', '**/*.properties')
}3. 命名方法作为调用:
一个流行的选项,只在 Groovy 中支持的是简写符号。
copy {
from("resources")
into("target")
include("**/*.txt", "**/*.xml", "**/*.properties")
}| 此选项破坏了任务配置避免,不推荐使用! |
无论选择哪种方法,任务都配置了要复制的文件名和文件位置。
3. 实现任务
Gradle 提供了许多任务类型,包括 Delete、Javadoc、Copy、Exec、Tar 和 Pmd。如果 Gradle 没有提供满足您构建逻辑需求的任务类型,您可以实现自定义任务类型。
要创建自定义任务类,您需要扩展 DefaultTask 并将扩展类设为抽象。
abstract class MyCopyTask : DefaultTask() {
}abstract class MyCopyTask extends DefaultTask {
}